Describe How Muscles Contract and Relax.
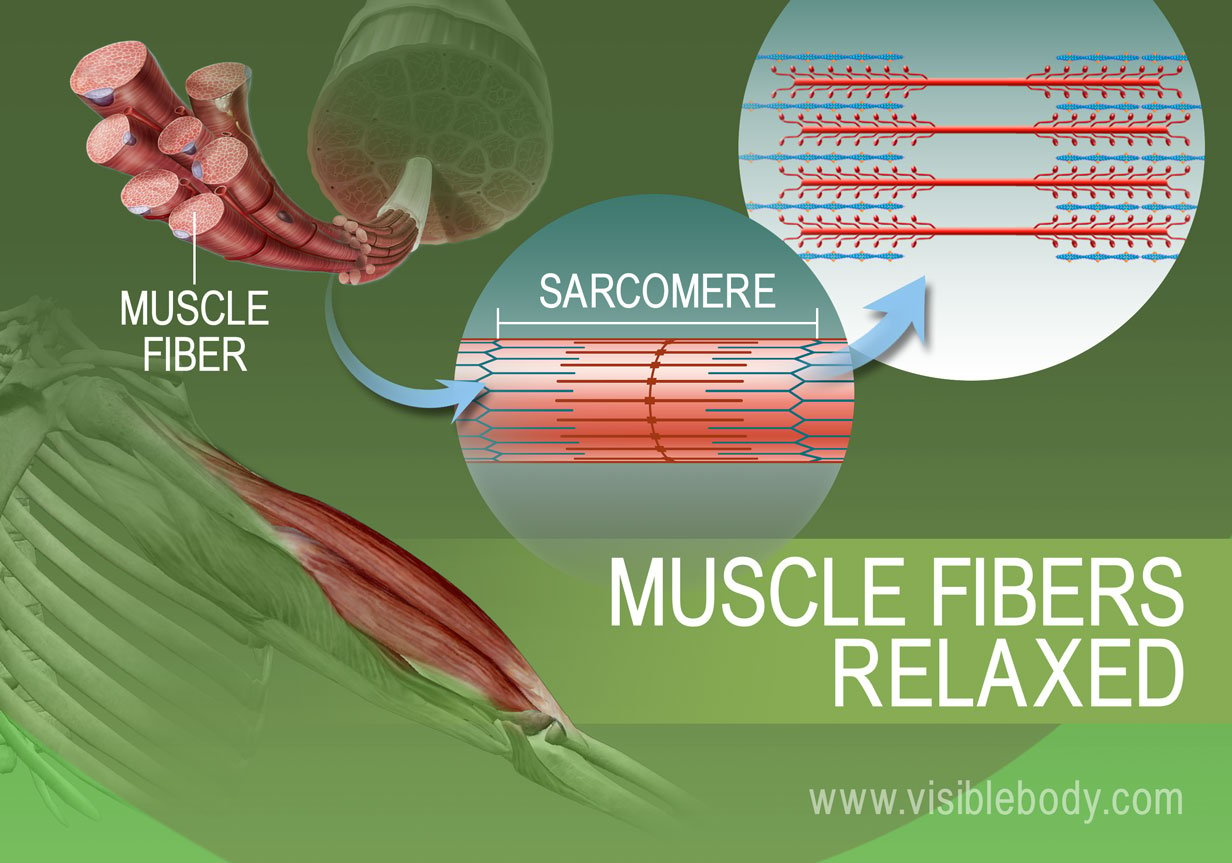
This makes the sarcomeres shorter and thicker contracting the muscle. Groups of thick and thin filaments that alternately overlap and move apart are called sarcomeres.
Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
Calcium floods into the muscle cell binding with troponin allowing actin and myosin to bind.
. Calcium binds to troponin. Muscle contraction occurs when the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slide past each other. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. It is generally assumed that this process is driven by cross-bridges which extend from the myosin filaments and cyclically interact with the actin filaments as ATP is hydrolysed. This is the power stroke.
View the full answer. Myosin head groups attach to the surrounding actin filaments forming a cross-bridge. Explain how muscles work with tendons to move the body 4.
But you can make a fist and that is tense -. Start studying Unit 3 How Does a Muscle Contract and Relax. The muscles are made of long string like structures they are called actin and myosin.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. When the CNS sends a signal the thick and thin myosin filaments form a crossbridge pattern by sliding past each other. When relaxation begins the opposing muscle contracts and pulls the original contracting muscle back into place.
Muscles are attached to bones by tendons and help them to move. 100 1 rating Muscle are made up of actin and myosin. The motor nerve stimulates an action potential impulse to pass down a neuron to the neuromuscular junction.
Ca ions are pumped back into the SR which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. Once your muscle contracts the space between the motor end plate and the fibers releases an enzyme called acetylcholinesterase which ends the stream of action. Muscle Contraction Steps in Detail.
Calcium is released from the terminal cisternae into the muscle fiber. All muscles are made up of two contractile proteins called actin and myosin. The Sliding Filament Theory and How Muscles Contract Fast Facts.
Define the process of muscle metabolism. Skeletal muscle is attached to bone through tendons and it contracts or relaxes in order to move the bone that it is connected to. Open channels allow an influx of sodium ions into the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber.
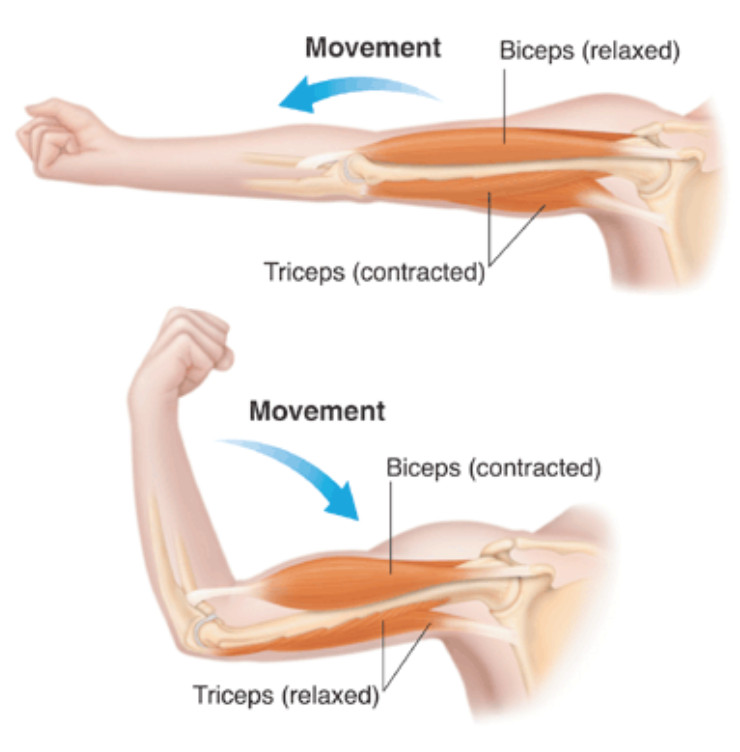
A muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of ATP and becomes fatigued. Muscles can work in antagonistic pairs so that when one muscle contracts the other relaxes. The sodium influx also sends a message within the muscle fiber to trigger the release of stored calcium ions.
Explain the organization of muscle tissue 2. Skeletal muscle is the type of muscle used for physical movement such as when we pick up objects or go for a run. During contraction and relaxation the length of the filaments.
Describe the function and structure of skeletal cardiac muscle and smooth muscle 3. A signal is sent from the brain or. Acetylcholine binds with receptors on the cell membrane on the muscle fiber opening Ca2 -Na channels.
What are the steps in muscle contraction. Explain how muscles work with tendons to move the body 4. The head group then bends causing the think filament to be pulled along and so overlap more with the thick filaments.
Explain how muscles contract and relax. Usually referred to as Calcium channels. Explain how muscles contract and relax.
The release of calcium ions initiates muscle contractions. Who are the experts. This causes the muscle to stop contracting and begin relaxation.
When acetylcholine reaches receptors on the membranes of muscle fibers membrane channels open and the process that contracts a relaxed muscle fibers begins. Describe what is involved in muscle contraction. When a muscle contracts bunches up it gets shorter and so pulls on the bone it.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. The actin and myosin cross bridges bind and. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction.
The primary mode of action for muscle is by contraction. The contractions and relaxation done by. This stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium into the muscle cell.
Troponin shifts tropomyosin which was blocking the active site on the actin. The sequence of events that result in the contraction of an individual muscle fiber begins with a signalthe neurotransmitter AChfrom the motor neuron innervating that fiber. The sequence of events that result in the contraction of an individual muscle fiber begins with a signalthe neurotransmitter AChfrom the motor neuron innervating that fiber.
Groups of actin and myosin form myofibrils which group together to form a muscle fiber which group together to form a fascicle which group together to form the whole muscle. The relative movement of thick and thin filaments causes muscles to contract and relax. Relaxation of a Muscle Fiber.
One is a head on a spring the other like a saucer. The local membrane of the fiber will depolarize as positively charged sodium ions Na enter triggering an action potential that spreads to the. This is contraction.
When they connect - you have a tense muscle. The areas between the thick and thin filaments during a relaxed state are called I bands H zones and A bands. Describe how muscles contract and relax 5.

Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Lifetime Fitness And Wellness

Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Lifetime Fitness And Wellness

Muscle Contraction And Movement In Animals Body Movements Class 6
No comments for "Describe How Muscles Contract and Relax."
Post a Comment